The ICT and digitalisation capability map encompasses all the capabilities needed for a high-performance public administration. Structured into 12 domains, it focuses on what is required to support digital transformation and optimise workflows.
The ICT and digitalisation capability map covers the capabilities required by the Federal Administration. It applies to all federal departments and offices and can serve as a source of inspiration for any other organisation. It is divided into 12 distinct domains, each of which encompasses specific capabilities. The aim is to provide a framework for strategic and operational planning of ICT and digitalisation initiatives.
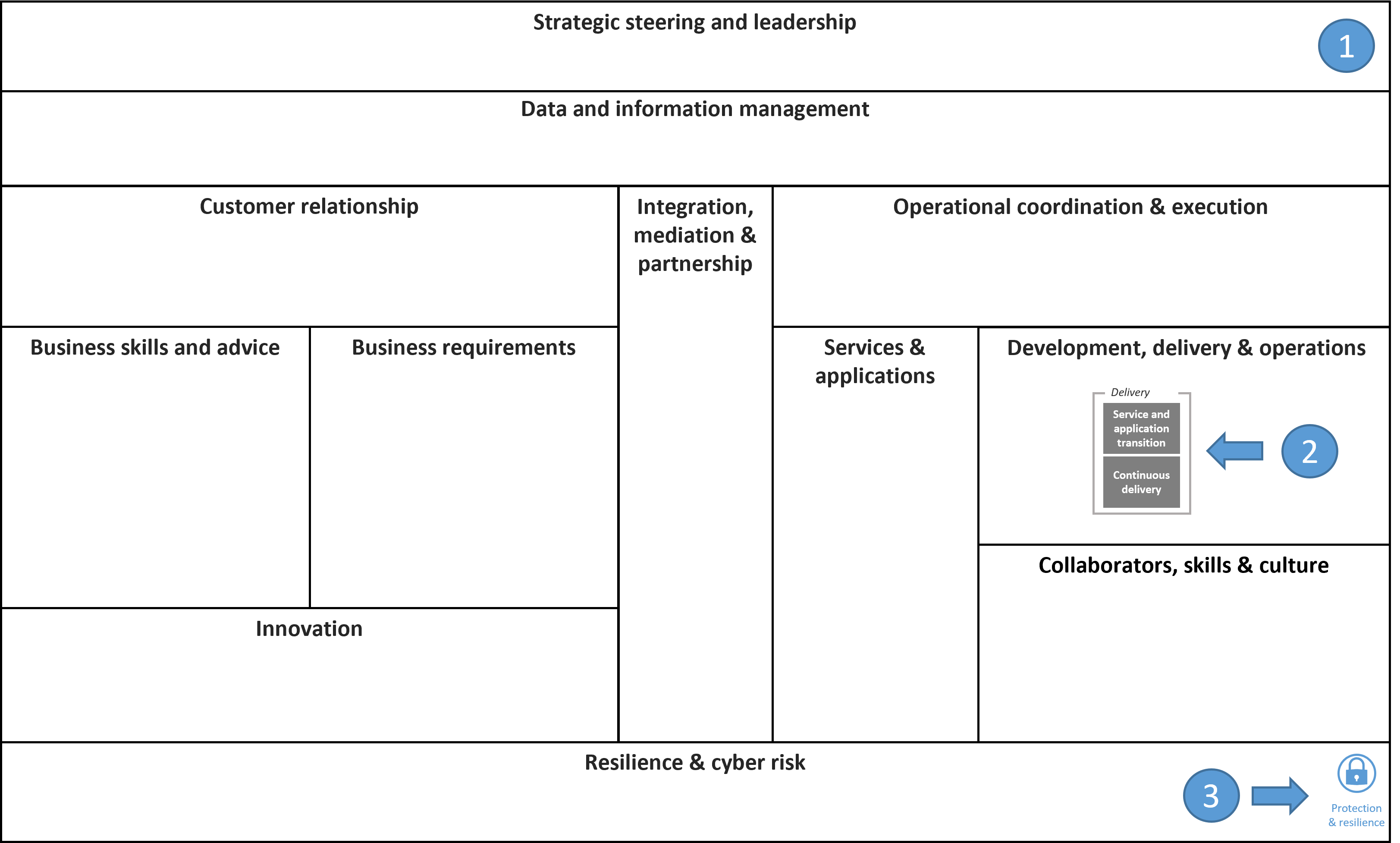
Structure of the capability map
1. Domains
The domains group together the capabilities needed by the Federal Administration in the context of IT and digitalisation. They are defined by the following characteristics:
- Each domain groups together capabilities with a similar theme, meaning they are logically linked from a functional point of view.
- There is a high degree of functional dependency within domains (internal homogeneity), which encourages intensive interaction between capabilities in the same domain.
- Domains are loosely coupled to each other, with limited interactions (external heterogeneity), which reduces dependencies between domains.
- The domain structure allows for stable planning and avoids overlap, as it focuses on the 'WHAT' rather than the 'HOW'.
2. Capabilities
Capabilities are subsets of domains and are located at a lower hierarchical level. They include the skills and resources needed for ICT and digitalisation in the Federal Administration:
- Each capability includes several dimensions such as employees, equipment, processes and information.
- Capabilities can have different levels of maturity and can be developed or improved over time.
- They are specific and detailed, covering the precise requirements for implementing digital technologies and processes.
3. Objects
The objects indicate the main elements managed or logically responsible within each domain:
- Each domain manages one or more specific objects that are essential to its function.
- These objects can be exchanged between domains according to the requirements of use cases, facilitating collaboration between different sectors of the Federal Administration.
This is a logic model which organises the domains and capabilities in such a way as to support ICT digitalisation and management in the Federal Administration. This structure enables the Federal Administration to manage its digitalisation resources and skills in a way that encourages collaboration between the various departments and offices.
Overview of capabilities
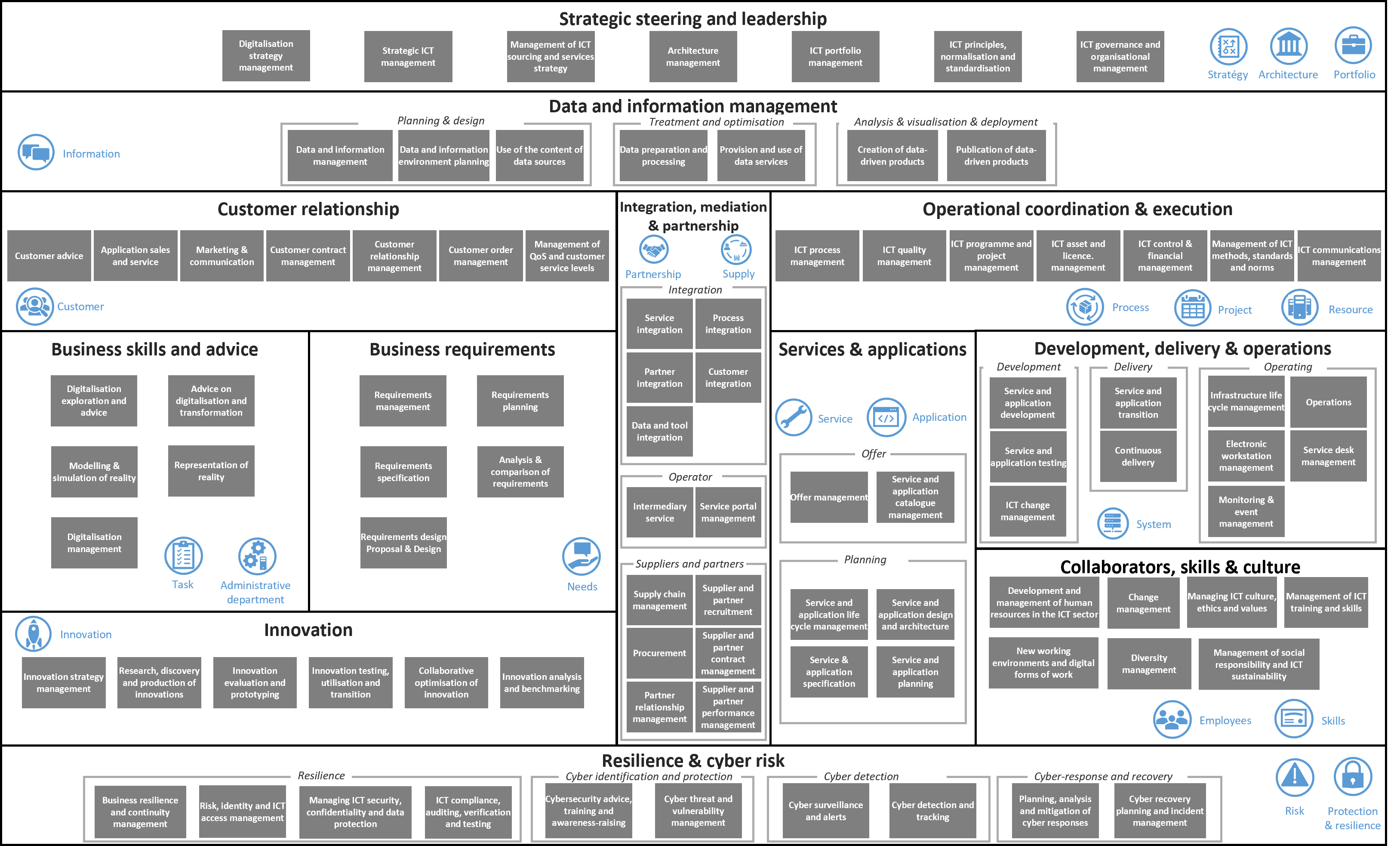
Strategic steering and leadership
Strategic steering and leadership covers the development and management of the digitalisation strategy, aligning the necessary initiatives with the overall vision. It defines ICT objectives to optimise administrative activities, while developing an ICT sourcing and services strategy. It also manages enterprise architecture in line with business requirements and aligns ICT investments with strategic objectives. Finally, it oversees the governance of principles, norms and standards, ensuring the efficiency and quality of ICT services.
- Digitalisation strategy management: Development and maintenance of a digitalisation strategy, integrating the overall vision and the necessary initiatives.
- Strategic ICT management: Definition of strategic ICT objectives to develop and optimise activities.
- Management of ICT sourcing and services strategy: Development and implementation of a strategy for selecting ICT service providers and designing the procurement of ICT services.
- Architecture management: Development and maintenance of enterprise architecture in line with business requirements.
- ICT portfolio management: Management of the ICT portfolio to ensure that investments are aligned with strategic objectives.
- ICT principles, normalisation and standardisation: Design and governance of principles, norms and standards for the operational use of ICT.
- ICT governance and organisational management: Analysis and implementation of ICT governance structures to ensure the efficiency and quality of ICT services.
Data and information management
Data and information management establishes standards and policies to ensure the ethical and effective management of data. It models and manages data flows to optimise business processes, while providing structured access via a catalogue. It guarantees data quality, compliance, storage and access, develops value-added products and publishes these products to maximise their usefulness.
- Data and information management: Establishment of standards and policies for effective and ethical data management.
- Data and information environment planning: Modelling and management of data flows for optimal use in business processes.
- Use of the content of data sources: Identifying and evaluating data sources and making them available to users via a data catalogue.
- Data preparation and processing: Organisation and maintenance of data to ensure quality and compliance with standards.
- Provision and use of data services: Provision and management .of data storage and access services to guarantee data availability.
- Creation of data-driven products: Development of value-added products from existing data to support business objectives.
- Publication of data-driven products: Publication and dissemination of data-driven products and information to maximise their usefulness.
Customer relationship
Customer relationship management collects and analyses information to understand and manage customer interactions. It aligns customer demands with available services and promotes the ICT organisation internally and externally. It manages customer contracts, including purchased services, and formalises relationships to improve customer satisfaction. Order management covers entry, delivery and status tracking. Finally, it monitors and manages the quality of services provided under service level agreements (SLAs).
- Customer advice: Gathering, analysing and making available the information needed to understand and manage customer interactions.
- Application sales and service: Management of customer requests and campaigns, aligning customer expectations with available services.
- Marketing & communication: Promoting the ICT organisation and its services, both internally and externally.
- Customer contract management: Complete management of contractual customer information, including acquired services.
- Customer relationship management: Formalised management of relations between customers and ICT departments to improve comprehension and satisfaction.
- Customer order management: Management of customer orders, from entry to delivery, including tracking of order status.
- Management of QoS and customer service levels: Monitoring and managing the quality of services provided against agreed service level agreements (SLAs).
Business skills and advice
Business skills and advice focus on identifying digitalisation opportunities and providing advice on their implementation. They provide support for the implementation of digitalisation initiatives and plan administrative activities using digital models and simulations to represent systems and technologies in administrative reality. Finally, they ensure the transparency and management of digitalisation technologies deployed within administrative processes.
- Digitalisation exploration and advice: Proactive identification of digitalisation opportunities and advice on their implementation.
- Advice on digitalisation and transformation: Advice on selecting and implementing digitalisation and transformation opportunities.
- Modelling & simulation of reality: Planning and modelling of administrative activities using digital models and simulations.
- Representation of reality: Representation of systems and technologies in administrative reality for better operational management.
- Digitalisation management: Transparency and management of digitalisation technologies deployed within administrative processes.
Business requirements
Business requirements management includes analysing and planning for the requirements of ICT customers to ensure an appropriate response. In collaboration with customer relationship management, it identifies emerging requirements, and it documents these requirements so that they can be managed throughout their life cycle. It analyses and compares requirements to identify potential solutions prior to acquisitions or developments. Finally, it develops and maintains design proposals to meet the specified requirements.
- Requirements management: Analysing, planning and documenting the requirements of ICT customers, ensuring an appropriate and coherent response.
- Requirements planning: Requirements planning in collaboration with customer relationship management to identify emerging requirements.
- Requirements specification: Detailed specification and documentation of requirements to ensure complete management of the requirements life cycle.
- Analysis & comparison of requirements: Analysis of requirements and identification of potential solutions prior to acquisitions or developments.
- Requirements design Proposal & Design: Development and maintenance of design proposals to meet specified requirements.
Innovation
Innovation strategy management covers the development and management of strategies for taking advantage of new technologies and trends. It identifies relevant innovations and verifies their feasibility through prototyping. Innovations are tested and implemented outside regular frameworks. Innovations are optimised in collaboration with customers and partners. Finally, analysis and benchmarking measure the implementation of innovations to achieve the defined objectives.
- Innovation strategy management: Developing and managing innovation strategies to take advantage of new technologies and trends.
- Research, discovery and production of innovations: Systematic research and identification of relevant innovations.
- Innovation evaluation and prototyping: Evaluation and prototyping of innovations to check their relevance and feasibility.
- Innovation testing, utilisation and transition: Testing and implementing innovations outside the regular testing framework.
- Collaborative optimisation of innovation: Development and optimisation of innovations in collaboration with customers and partners.
- Innovation analysis and benchmarking: Analysis and benchmarking of innovations to measure their degree of implementation and achieve the defined objectives.
Integration, mediation & partnership
Integration, mediation & partnership harmonises partner services to maximise efficiency. It manages processes between ICT suppliers and integrates partners and customers for better collaboration. Partners' data and tools are integrated, and services are mediated between suppliers and users. Portal management facilitates information exchange and communication, while procurement guarantees long-term delivery capacity, offering transparency in supplier recruitment. Contracts and partner relationships are managed and performance monitored.
- Service integration: Seamless integration of services provided by internal and external partners to maximise efficiency and added value.
- Process integration: Integration of processes across multiple ICT service providers for consistent management.
- Partner integration: Integration of partners with the necessary information and processes.
- Customer integration: Integration of customers into the supply chain for seamless collaboration.
- Data and tool integration: Integration of partner data and tools into the organisation.
- Intermediary service: Mediation of services between suppliers and users to add value.
- Service portal management: Management of information exchange and communication with customers and partners.
- Supply chain management: Ensuring long-term ICT supply chain and delivery capacity.
- Supplier and partner recruitment: Transparency and systematic selection of potential suppliers.
- Procurement: Optimised procurement of ICT resources.
- Supplier and partner contract management: Management of supplier and partner contracts throughout their life cycle.
- Partner relationship management: Managing relationships with partners and associated risks.
- Supplier and partner performance management: Monitoring and managing the performance of suppliers and partners.
Operational coordination & execution
Operational coordination & execution ensures the design and execution of ICT processes to guarantee continuity and quality. It focuses on the quality of processes and their results. ICT programme and project management coordinates initiatives aligned with the strategy. It covers the life cycle of assets and licences, including budgeting and cost control. In addition, the management of methods, standards and norms supports governance. Finally, it facilitates communication with stakeholders.
- ICT process management: Design, visualisation and efficient execution of ICT processes to ensure operational continuity and quality.
- ICT quality management: Quality assurance of ICT processes, methods and results.
- ICT programme and project management: Coordinated planning and management of ICT programmes and projects aligned with the strategy.
- ICT asset and licence. management: Complete management of ICT assets and licences throughout their life cycle.
- ICT control & financial management: Management of ICT-related financial activities, including budgeting and cost control.
- Management of ICT methods, standards and norms: Design and maintenance of ICT methods, norms and standards to support governance.
- ICT communications management: Facilitating and implementing effective and timely communication with stakeholders.
Services & applications
Services & applications management manages a variety of offerings to meet customer requirements. It develops catalogues and manages the entire life cycle of services and applications. Design and architecture are aligned with customer expectations, with precise specifications for development and testing. In addition, it plans the implementation, integrating the necessary infrastructure and the organisation of the operation for best possible performance.
- Offer management: Creation and management of service and application offerings to meet the needs of internal and external customers.
- Service and application catalogue management: Development and maintenance of service and application catalogues, providing detailed information on available services.
- Service and application life cycle management: Management of services and applications throughout their life cycle, from planning to decommissioning.
- Service and application design and architecture: Design and architecture of new services and applications, aligned with customer requirements.
- Service & application specification: Preparation of detailed specifications for the development and testing of services and applications.
- Service and application planning: Operational planning for the implementation of services and applications, including infrastructure and operational organisation.
Development, delivery and operations
Offer management in the development, delivery & operations domain creates and manages services and applications to meet customer requirements. It develops and maintains detailed catalogues covering every stage in the life cycle of services and applications, from planning to decommissioning. Design and architecture focus on creating new services aligned with customer requirements, with precise specifications for development and testing. In addition, operational planning integrates the infrastructure and organises operations to ensure efficient implementation of services and applications.
- Service and application development: Development and implementation of ICT services, products and applications.
- Service and application testing: Testing and validation of services and applications before they go live.
- ICT change management: Controlled management of changes to ICT systems and services in production.
- Service and application transition: Orderly transition of developed or modified services and applications to production.
- Continuous delivery: Continuous, automated delivery of services and applications in production.
- Infrastructure life cycle management: Management of ICT infrastructures throughout their life cycle.
- Operations: Management and supervision of day-to-day ICT operations.
- Electronic workstation management: Supply and management of electronic/digital workstations for employees.
- Service desk management: Management of user requests and incidents via a service centre.
- Monitoring & event management: Monitoring systems, services and applications to detect and manage operational events.
Collaborators, skills and culture
The collaborators, skills & culture domain covers the management of the life cycle of ICT employees, from recruitment to retirement. It ensures the successful implementation of organisational change and promotes diversity, ethics and values within the organisation. Training and skills development for ICT employees are essential, as is the creation of new digital and innovative working environments. Diversity management improves results thanks to a wider range of opinions and experiences. Finally, social responsibility and ICT sustainability incorporate concepts for improving the social, environmental and economic aspects of the organisation.
- Development and management of human resources in the ICT sector: Life cycle management of ICT employees, from recruitment to retirement.
- Change management: Managing organisational change to ensure successful and sustainable implementation.
- Managing ICT culture, ethics and values: Promoting diversity, ethics and values within the ICT organisation.
- Management of ICT training and skills: Management of training and skills development for ICT employees.
- New working environments and digital forms of work: Development of new working environments and digital forms of work.
- Diversity management: Diversity management to improve work results through a wider range of opinions and experiences.
- Management of social responsibility and ICT sustainability: Integration of concepts and tools to improve the organisation's social, environmental and economic aspects.
Resilience and cyber risk
Resilience & cyber risk ensures business continuity and resilience in the face of disruption. It manages ICT risks, identities and access, while ensuring the security, confidentiality and availability of information. ICT compliance ensures that laws and standards are respected, while cybersecurity advice offers training and awareness-raising. Threat and vulnerability management identifies and deals with cyber threats. Cyber surveillance detects incidents, and cyber tracking investigates them. Finally, response planning and incident recovery ensure the recovery of systems and data.
- Business resilience and continuity management: Planning and implementing business continuity and resilience to disruption.
- Risk, identity and ICT access management: Identification, assessment and management of ICT risks, including identity and access management.
- Managing ICT security, confidentiality and data protection: Guaranteeing the confidentiality, integrity and availability of information and ICT systems.
- ICT compliance, auditing, verification and testing: Monitoring and validating compliance with laws, regulations and ICT standards.
- Cybersecurity advice, training and awareness-raising: Advice, training and awareness-raising on cybersecurity for internal and external stakeholders.
- Cyber threat and vulnerability management: Identifying and managing cyber threats and vulnerabilities.
- Cyber surveillance and alerts: Continuous monitoring of ICT systems to detect security incidents.
- Cyber detection and tracking: Detection and investigation of ICT security incidents.
- Planning, analysis and mitigation of cyber responses: Planning and implementing responses to cybersecurity incidents.
- Cyber recovery planning and incident management: Planning and managing the recovery of systems and data following a cybersecurity incident.
Further information
Contact
Federal Chancellery
Digital Transformation and ICT Steering DTI Sector
Monbijoustrasse 91
3003 Bern
- Tel.
- +41 58 463 46 64





